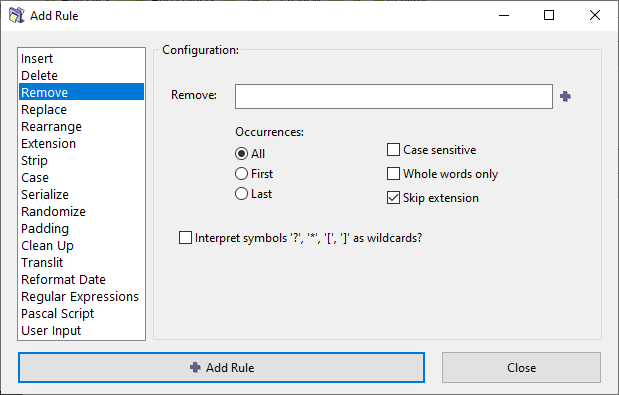
ReNamer › Rules › Remove rule
This rule removes the specified string from the file name. It has options to remove the first occurrence, the last occurrence, or all the occurrences of the specified string. You can enter multiple strings at a time (just separate them with *|*). If ReNamer finds any of them in the name, they will be removed. You can create a pattern with wildcards, so that any string that matches the pattern will be removed.
The parameters are as follows:
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Remove | Enter the string to be removed.
TIP: Sometimes, the file names have a common string that needs to be removed. In such cases, rather than entering the whole string by hand, it is easier to borrow it from one of the file names. To do this, just click on a file name in the Files pane of ReNamer BEFORE launching the Remove rule. ReNamer will automatically copy the entire name of the selected file into the Remove field. Now edit this entry to get the desired common string. |
| Inserts a separator (*|*) sequence between two delimiter entries. (You can directly type *|* instead of clicking on this button.) | |
| Occurrences | In case the strings occur multiple times in the name, specify which occurrences should be removed. (Options are: first only, last only, or all) |
| Skip extension | If checked, the file extension will be excluded from the processing and will remain unaffected. |
| Case sensitive | Will only remove a specified string from the name if the case matches exactly. |
| Whole words only | Remove the subject text only when it is whole word, not a part of another word.
For example, searching for "bar" would not find a match in "foobar" or "bars". |
| Interpret symbols as wildcards | Treat certain symbols as Wildcards for matching simple patterns (similar to Regular Expressions). |
Wildcards
| Wildcard | Represents | Example |
|---|---|---|
| any number of characters (including numbers, space, underscores, etc.). | abc* equals abc followed by 0 or more characters. | |
| Any single character (including numbers, space, underscores, etc.) | ab?d equals abcd, ab1d, ab d, ab_d, etc. | |
| Brackets enclose a set of characters, any one of which may match a single character at that position. | foo[ab]ar equals fooaar and foobar | |
| (only within a pair of brackets) denotes a range of characters. | foo[a-z]ar equals fooaar, foobar, foocar, foodar, etc. |