ReNamer:Pascal Script:Quick guide
If you are not familiar with Pascal Scripting, first go through the excellent tutorial written by Tao Yue:
The following is a short overview of Pascal Script.
Basic pascal script
The structure of a basic script is as follows:
PROGRAM
ProgramName (FileList);
CONST
<Constant declarations>
TYPE
<Type declarations>
VAR
<Variable declarations>
<definitions of subprogram>
BEGIN
<Executable statements>
END.
Control Structures
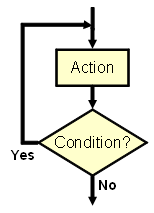
All the typical control structures (building blocks) occurring in Pascal Script are described in the following table.
The table shows a flow chart and Pascal Script code required to implement that logic. You can simnply copy and paste these blocks and then edit them to finish your script.
In actual implementation, just substitute the following:
- Replace <condition> with an actual Pascal statement that tests for a condition.
- Replace <Action> with code block that takes action relevant to the condition. There may be several statements.
| Comments | |||
|---|---|---|---|
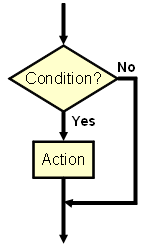
| if <condition> then
begin <Action> end; |
Executes the <Action> statement only if the <Condition> is met. Otherwise pass on the control to the next statement. | ||
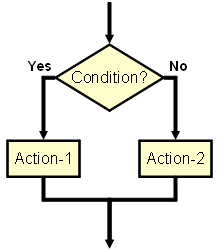
| if <condition> then
begin <Action-1> end else begin <Action-2> end; |
Two alternative actions are provided. If <Condition> is met, execute <Action-1>. Otherwise execute <Action-2>. Thus one of these two <Actions> are definitely executed. | ||
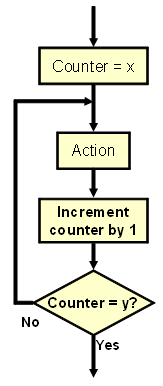
| for I:=x to y do
begin <Action> end; |
To execute the <Action> a certain number of times. This example shows that the counter is incremented by 1 only, but it can be any statement that changes the value of counter towards the target value. | ||
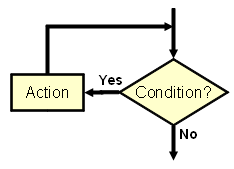
| while <condition> do
begin <Action> end; |
Checks for a condition and if it is met, executes an<Action>. The loop is repeated till the condition is met. When the condition is not met the control passes to the next statement. Note that if the condition fails in the first-ever check, the <Action> may not be executed at all. Make sure that the condition will fail at some point of time; otherwise the loop will execute endlessly, and ReNamer will appear to be hung. Sometimes the condition is set to be always TRUE, and then a statement inside the <Action> block breaks the loop based on a different condition. | ||
| Repeat until | repeat
<Action> until <condition>; |
This structure is similar to the While loop (see above). However, the only difference is that the <Action> is taken first and then the condition is checked. As a result, the <Action> is executed at least once. | |
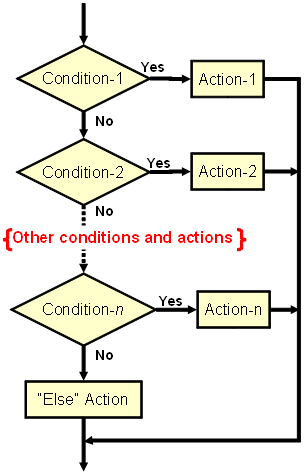
| case x of
<Action-1> Break end;
<Action-2> Break end;
<Default Action> end;
|
This is a generalized version of the if-then-else block (see second row above). | ||
| case x of
<Action-1> end;
<Action-2> end;
<Default Action> end;
|
This is similar to the case structure above, but here, all the conditions are checked, and if any condition is met, the corresponding <Action> is execurted. The code structure has a default action that is always executed, regardless of whether any of the conditions are met. After that, the control is apassed to the next statement.
This structure is equivalent to a series of if-then blocks (see the first row), PLUS a default <Action> block. | ||
|
This statement is placed in any of the above blocks to break any of the loops when a condition is met. Typically, it is used in a if-then block that is embedded (nested) inside the other code block. See the Case block above, which uses the break statement as integral part of its structure. | |||
|
This statement is placed in any of the above loops to jump to the end of the current iteration, bypassing all the subsequent statements within the loop. However, the execution of the loop continues (a fresh iteration starts). Typically, it is used in a if-then block that is embedded (nested) inside the other code block | |||
|
This statement is placed in any of the above loops to jump to the end of the current iteration, and terminate the loop. The control passes to the the next statement Typically, it is used in a if-then block that is embedded (nested) inside the other code block |